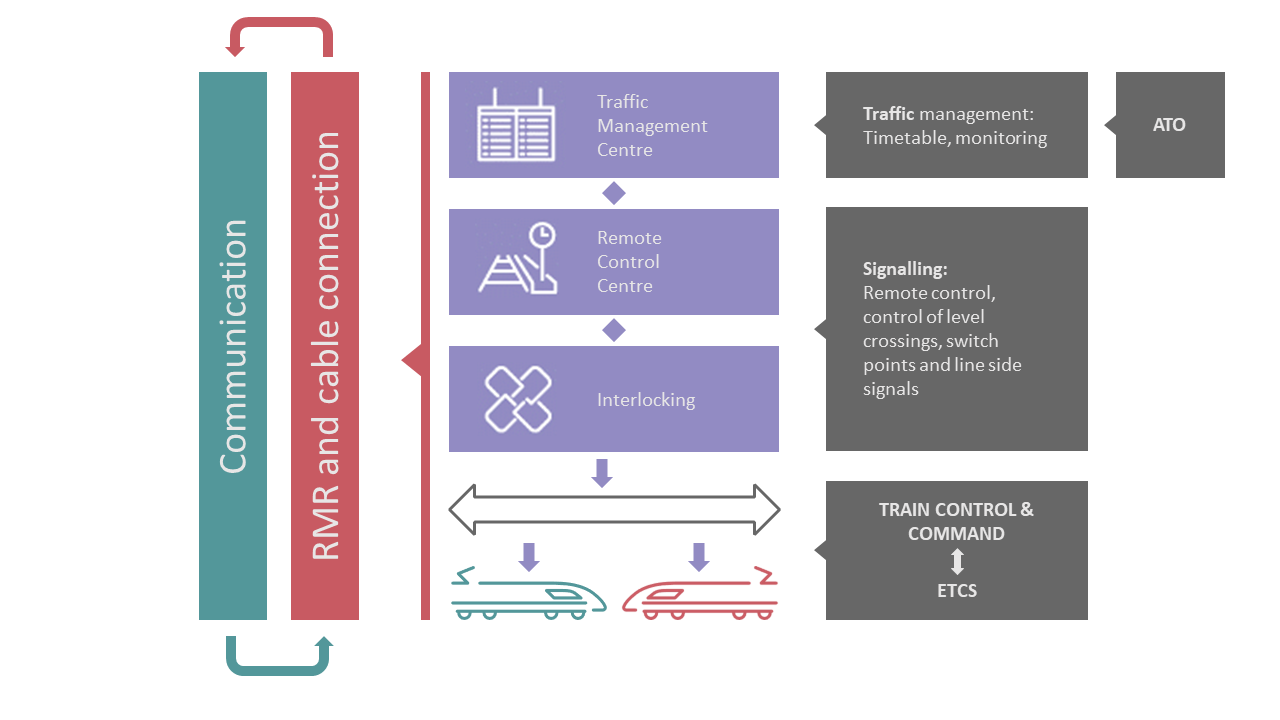
ERTMS is comprised of three systems:
- ETCS (European Train Control System) is a train control standard, based on in-cab equipment able to supervise train movements, including stopping the train, according to the maximum permitted speed at each line section. Information on track description is received from the ETCS equipment installed beside the track, Eurobalises or radio (depending on the operational level) and used to calculate and supervise the maximum speed at all times. The driver’s response is continuously monitored, and if necessary, the train’s emergency brakes can be engaged by ETCS.
- RMR (Railway Mobile Radio) is the European radio communications system for railway operations and the second of the three ERTMS systems. It is comprised of two radio systems: GSM-R (Global System for Mobile Communications - Railways) and FRMCS (Future Railway Mobile Communication System). The two systems may be implemented both at the same time or each of them independently. RMR facilitates the communication between the train and the traffic control centres located besides the track.
- GSM-R is based on GSM radio technology and uses exclusive frequency bands.
- FRMCS is the future telecommunication system for railways and based on 5G technology. It is designed as the successor of GSM-R and is hereby a key enabler for the digitalisation of rail transport.
- ATO (Automatic Train Operation) is the third ERTMS system and automates the operation of the train up to Grade of Automation 2 (GoA2). ATO at GoA2 starts and stops the train automatically with ETCS providing the automatic train protection (ATP) functionalities, which monitors train movements and speed limits on the line.