The ERTMS system is divided into 2 subsystems: on-board (green boxes) and trackside (red boxes), as shown in the figure below.
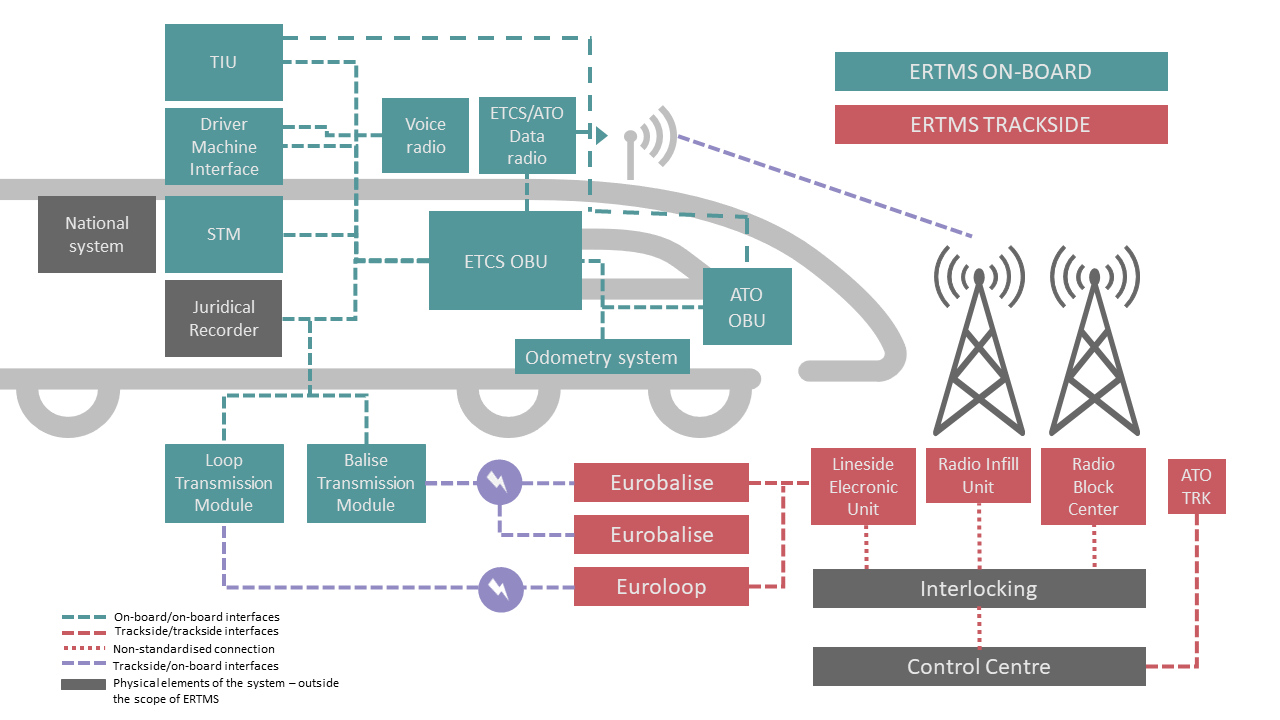
The ERTMS components corresponding to the ERTMS subsystem installed are:
(a) on the trackside
Control Centre
The Control Centre is not an ERTMS component. It is a signal box covering all the routes and trains running in a specific area. A Control Centre usually commands several interlockings, comprising one or several railway lines.
Eurobalise
The Eurobalise is a passive device that is installed on the track, storing data (fixed or switchable, i.e. with the possibility of changing information content) related to the infrastructure, such as speed limits, position references, gradients, etc. It is a passive device as it does not need an electric supply since it is the train antenna (BTM) that energises it when passing over it.
Euroloop
The Euroloop is a semi-continuous, intermittent transmission system. It provides signalling in-fill information in advance as regards the next main signal in the train running direction as soon as they become available.
Interlocking
Interlocking is not an ERTMS component, but it plays an essential role in the signalling system. Interlocking is an equipment that guarantees safety for train movements or routes by monitoring the setting and releasing of signals and points and ensures that the route for a specific train is established and that incompatible routes are not simultaneously established. The interface between the interlocking and the ERTMS trackside subsystem is necessary in almost all ERTMS structures.
Lineside Electronic Unit (LEU)
The LEU is an electronic device which is used as the interface between the Eurobalise and interlocking (see below). The LEU acquires the information from the interlocking and, in concordance with the lineside signalling (if available), sends the appropriate information (called a 'telegram') to the Eurobalises, which in turn send it to the onboard system.
Radio Block Centre (RBC)
The RBC is a device used at ETCS Level 2 acting as a centralised safety unit. Using radio connection via GSM-R, it receives train position information and sends movement authority and further information required by the train for its movement. The RBC interacts with the interlocking to obtain signalling-related information, route status, etc. It is also able to transmit selected trackside data and communicate with adjacent RBCs.
Radio Infill Unit (RIU)
The RIU is a component that may be part of the ETCS Level 1 to increase system performance. It allows the message contained in a Eurobalise to be sent in advance to the train by GSM-R transmission. Thus, a train located in the coverage area of the radio infill can constantly receive updated information, e.g. if the route is established and the train is authorised to proceed, this information will be received by the onboard system without the train needing to read the balise located at the signal.
(b) Among onboard components, the following can be mentioned:
Automatic Train Operation (ATO)
The ATO is the system that automates the operation of the train up to Grade of Automation 2 (GoA2). ATO at GoA2 starts and stops the train automatically with ETCS providing the automatic train protection (ATP) functionalities, which monitors train movements and speed limits on the line. There are both ATO system trackside (ATO TRK) and on-board (ATO OBU). The ATO trackside sends to the ATO OBU the information on the train’s timetables and, if the ATO conditions are meet (e.g. route information is available on-board), ATO OBU starts and stops the train automatically.
Balise Transmission Module (BTM)
The BTM is a module inside the ETCS onboard equipment for intermittent transmission from track to train, which processes signals received from the onboard antenna and retrieves data messages from a Eurobalise.
Driver Machine Interface (DMI)
The DMI is the interface between the driver and the ETCS. In most cases, it is a Liquid-Crystal Display (LCD) touch screen panel for control and indication functions, allowing the driver to enter data into the system (e.g. the driver identity or the train running number) and to visualise the output data (e.g. the permitted speed).
ERTMS/ETCS ON-BOARD EQUIPMENT
ERTMS/ETCS On-board equipment refers to the component, which can be software, hardware, or both, within the train's on-board system. This component is designed to meet the requirements specified by ERTMS/ETCS.
ETCS/ATO data radio
The “data radio communication” part of the Onboard control command and signaling subsystem is the radio system satisfying the mobile communications needs of the European railways, to provide safe communication between ETCS/ATO onboard and ETCS/ATO trackside for data services.
Juridical Recording Unit (JRU)
The Juridical Recording Unit provides ‘black box’ functions, i.e. it stores the most important data and variables from train journeys, allowing later analysis.
Loop Transmission Module (LTM)
The LTM is an optional module inside the ETCS onboard equipment for transmission from track and train, which processes signals received from the onboard antenna and retrieves data messages from a Euroloop.
National system
The National Train Control (Class B) system is the Automatic Train Protection (ATP) System required on-board to operate on infrastructures only equipped with a Class B system (e.g. LZB, PZB, KVB, ASFA…). On lines equipped with ERTMS, there is no need for an on-board national Class B system to operate.
Odometry system
The odometer is responsible for calculating the distance, speed and acceleration of a train, typically consisting of two technologies tachometry and radar.
Specific Transmission Module (STM)
The STM is a device that allows the ETCS onboard equipment to act as interface with the onboard part of an existing National Train Control (Class B) system. It enables smooth transitions from/to the national system(s) and gives access to some ETCS onboard devices (e.g. DMI – Driver Machine Interface).
Depending on its functionality and the desired configuration, the national system can be accessed either via an STM using the standard interface or via another national solution.
Train Interface Unit (TIU)
The TIU is the unit, inside the ERTMS/ETCS on-board equipment, that provides the interface between the ETCS and the train to exchange information (e.g. the direction of the train movement) and to issue commands to the rolling stock (e.g. ETCS sends the rolling stock the command to apply the brakes).
Voice radio
The “voice radio communication”, part of the Onboard control command and signaling subsystem, is the radio system satisfying the mobile communications needs of the European railways, to provide safe communication between ground and train for voice services.




